A bad oxygen sensor will cause a wide range of symptoms and issues in your car. The best way to ensure that your vehicle is running at optimum efficiency is to have a functioning O2 sensor.
There are a variety of ways to test an O2 sensor. Using the OBD2 scanner is the easiest and most effective way to check your sensor.

What is an O2 sensor?
The O2 sensor is an electronic device used to monitor the oxygen level in your car’s exhaust stream after combustion. Because all combustion engines need a mix of oxygen and fuel to run, it is essential that we can track the fuel/oxygen ratio to give it the best working condition.
Hence, the O2 sensor plays an important role to make sure your car’s engine work properly and boosting fuel economy.
What does an O2 sensor do?
Oxygen sensors are one of the critical components of a car’s emission system. Cars from the late 1970s onward have these sensors. It is located on the exhaust manifold. Its job is to monitor oxygen levels. The system controls the amount of unburned oxygen and calibrates the fuel mixture accordingly.

Credit: upload.wikimedia.org
The O2 sensor indicates changes in the “richness” or “leanness” of a car’s emission operation. Burning rich means running on too little oxygen. Alternatively, running lean means that there is too much oxygen.
In essence, the O2 sensor is what helps to calibrate the proper fuel mixture for your car.
Types of O2 sensors
There are a wide variety of different O2 sensors on the market. The construction varies, but they serve the same overall function. Sensors will fall under three main categories. These are zirconia sensors, titania sensors, and wideband sensors.
Zirconia sensors

Credit: upload.wikimedia.org
Most likely, you are working with a zirconia sensor. Zirconia is the most common type of O2 sensor. Sensors are heated or unheated.
Unheated sensors are the original style and are still used today. The unheated sensor uses the heat from the exhaust to warm up. They cool down quickly and are thus not the most efficient type.
The heated sensors, as the name implies, contain a heating circuit. The sensors are warm as soon as the car starts. When properly heated, the sensor sends more reliable information to the computer.
Titania sensors
The titania type of O2 sensor is made from a different kind of ceramic than the zirconia style. It works quite a bit differently than a traditional sensor. It isn’t an option for many makes and models of cars.
Titania sensors do not send signals in the same manner. A zirconia sensor creates voltage. A titania sensor lowers or raises resistance depending on whether the fuel is rich or lean.
Wide band sensors
Wide Band sensors are a rather uncommon type of sensor. Most often these are found on new model cars. It is highly efficient at getting the perfect fuel mixture for different driving conditions.
High voltage manages the gas and oxygen ratios.
What causes an oxygen sensor to fail?
There are quite a few reasons that an oxygen sensor may fail. Like all parts of a car, they undergo wear and tear. Looking at the image, we can see what does a bad O2 sensor looks like.

Credit: as2.ftcdn.net
One of the most common causes of a failing O2 sensor is the build-up that reduces the efficiency of the sensor. Heat also plays a huge role. Steam and heat can take their toll on these sensors, causing them to make reading mistakes, which leads to problems with the fuel mixture.
Bad O2 sensor symptoms
Your car will display several symptoms when the O2 sensor is bad. The most common symptom is that the check engine light will come on. The light is not particularly helpful as it will come on for a range of different reasons.
Check engine light on

Credit: upload.wikimedia.org
Bad fuel mileage is another common symptom. You get poor fuel mileage due to improper fuel mixtures, which reduce the efficiency with which the vehicle operates. It can sometimes be accompanied by a sulfuric or rotten egg smell.
A car that starts to misfire is another symptom of a bad O2 sensor. Additionally, it may run roughly when idling. Performance problems like sluggishness and a loss of power are also common symptoms of a bad oxygen sensor.
How to test O2 sensor with OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool that connects directly to your vehicle. The following steps will help you work through the diagnostic process.
OBD2 scanner

Credit: upload.wikimedia.org
Step 1: Connect OBD2 scanner and DLC
Firstly, you want to connect the OBD2 scanner through the diagnostic link connector (DLC). It is triangular and has 16 pins. Check your owner’s manual or the internet if you are unsure where to locate the DLC.
Step 2: Connect OBD2 scanner to your vehicle
While the OBD2 scan tool is connected to your vehicle, you should take note of the O2 sensor voltage with the Engine Running and with the Engine Off. Also, please remember that the O2 sensor voltage will change when you take a ride, the typical value is from zero to 1 volt.
For around 10 minutes, O2 sensor voltage will fluctuate as you drive. On new models of air/fuel ratio sensors, they have different operations based on manufacturers. For example, some models work with varying amperage and some models work with varying voltage.
Step 3: Pay attention to the fluctuation of your O2 sensor voltage
In this step, you should take note of how quickly the O2 sensor voltage fluctuates from less than 0.5 V (low voltage) to more than 0.5 V (high voltage). There will be fluctuations or toggles that occurs several times a second.
Assuming your O2 sensor voltage is high (over 0.5 V), it indicates that there would be a rich exhaust code set. In contrast, your O2 sensor voltage stays low (lower than 0.5 V), it means that there would be a lean exhaust code set.
O2 sensor voltage chart
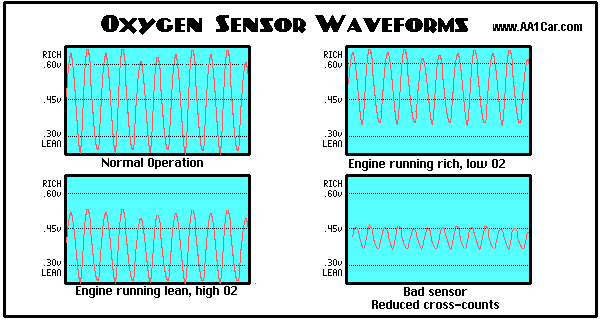
Credit: AA1Car.com
Step 4: Turn on your engine
You turn on only the ignition, not all the way. Doing so allows communication between the car and the diagnostic tool.
Step 5: Check codes on OBD2 scanner
Now, go to the menu and select ‘codes’ or ‘trouble codes.’ You then choose the system you need to diagnose. You will see two different types of code. These are pending and active codes.
Step 6: Diagnose problem
Lastly, you diagnose your problem based on these codes. The codes are easily searchable online and will provide all the information you need about repair or replacement.
FAQs
❓ Can a bad O2 sensor cause poor acceleration?
💡 Yes, one of the first noticeable symptoms of a bad oxygen sensor is reduced performance and sluggishness.
❓ Can a bad O2 sensor cause gas smell?
💡 A car that is running too rich will often emit a gas smell. A bad sensor may also cause a rotten egg smell.
❓ Is it OK to drive with a bad oxygen sensor?
💡 You should avoid driving with a bad sensor. Any untreated problem, it will continue to get worse and may cause other issues with your vehicle.
❓ Can a bad O2 sensor cause shake?
💡 Yes, and this is most noticeable when the car is idling. Rough idling is one of the most common symptoms of a bad sensor.
❓ Will a bad O2 sensor cause sputtering?
💡 Yes, an improper fuel mixture will cause the vehicle to sputter and may even cause it to backfire.
❓ Can a bad O2 sensor cause a car to run rich?
💡 Yes, the sensor’s job is to calibrate the proper fuel mixture for your vehicle. If the sensor is wrong, it may not correctly calibrate that mixture and could cause it to run rich or lean.
❓ When to replace O2 Sensors?
💡 A lousy sensor needs replacement. If your car is showing signs of a bad sensor, follow the instructions for diagnosis above or take it to an auto parts store that offers diagnostic tools. For vehicles that were made before 1990, replace the sensor about every 45,000 miles. For newer model vehicles, replacement should take place about every 65,000 miles.
Bottom line
That is how to test the O2 sensor with an OBD2 scanner and relevant information. We hope that this article is useful and you learn something that can help you solve your vehicle issue. Good luck!



Does not indicate how to check voltage to O2 sensor with scanner connected.
Thank you for your feedback. We will work on improving this.